

Microcontrollers run their programs from much smaller internal memory called the flash memory. Some CPUs have architectures that support different bit sizes within various components, including the internal memory and registers. Whatever determines the bit size of a microprocessor is not the largest register, bus, or ALU. However, that is no longer the case with modern microprocessors and microcontrollers. Traditionally, an N-bit CPU has an Arithmetic and Logic Unit (ALU), buses, or registers having N-bits.
The data size that a microprocessor handles in a single cycle is more significant than that of a microcontroller.ĭata in microcontrollers is in bits and bytes. On the other hand, microprocessors are 32-bit and 64-bit. For instance, microcontrollers are either 8-bit, 16-bit, or 32-bit. They perform complex tasks by communicating through USB, UART, and high-speed Ethernet.īoth microprocessors and microcontrollers can handle the same amount of data for the lower bit sizes.
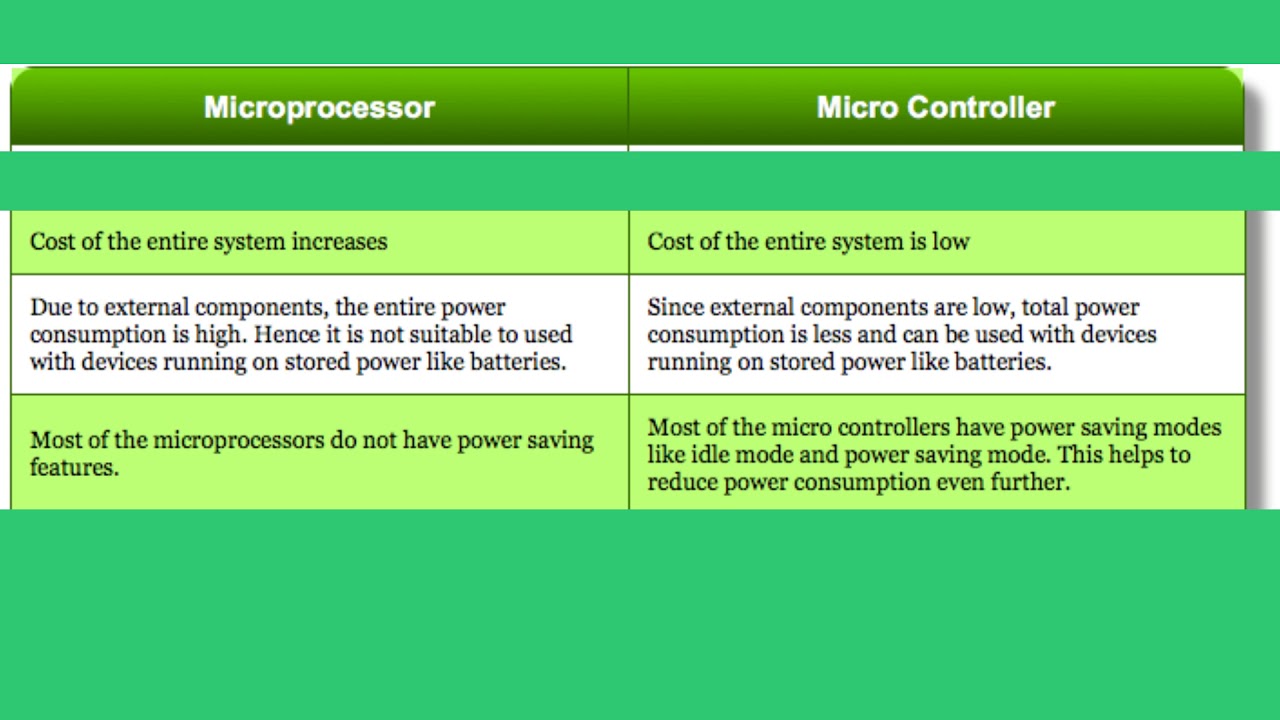
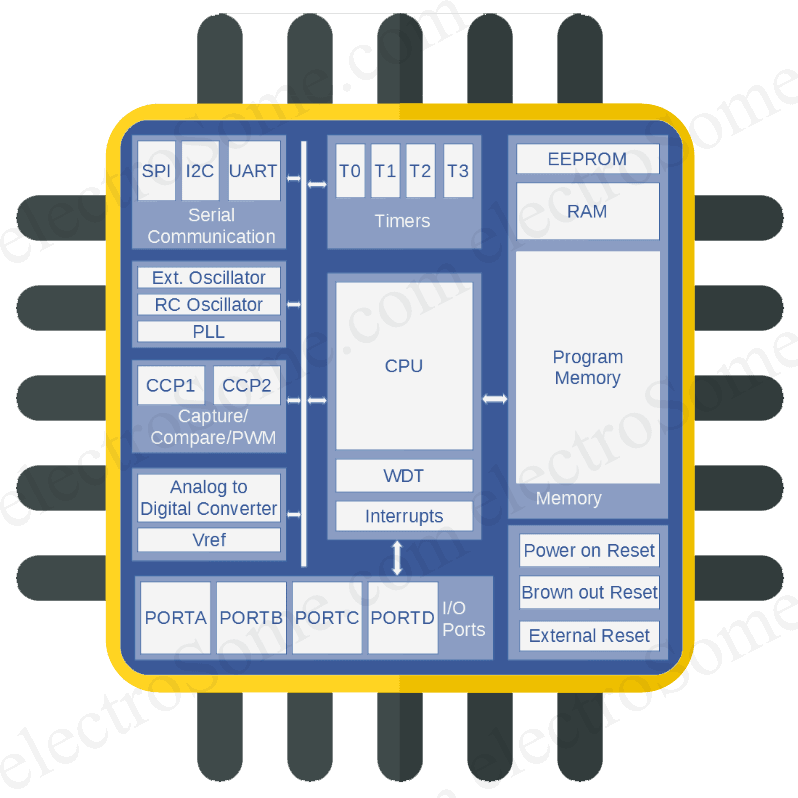
Microcontrollers use 12C, SPI, and UART as the standard hardware interfaces for performing a dedicated task. Communicating with these peripherals requires a channel that facilitates the flow of data and instructions. Microcontrollers and microprocessors rely extensively on peripherals such as sensors and shift registers for effective performance. Microprocessors are generally physically bigger than microcontrollers since they need more ports to interface with the peripherals. It is challenging, at times, to differentiate between a microcontroller and a microprocessor on size. Internal Parameters Of Microcontroller Vs. You can use a microprocessor in a variety of applications by selecting the peripherals you need. Its peripherals and memory components, like ROM and RAM, are connected externally. They are suitable for specific tasks and have fewer external components.Ī microprocessor houses and performs the essential computer CPU functions. The amount of memory and ports required for microcontrollers is limited. All peripherals such as watchdog timers, 12C, ADC, etc., and memory is housed with the CPU in one chip. The Structural Difference Between A Microcontroller And A MicroprocessorĪ microcontroller is a structurally more compact electronic component than a microprocessor.
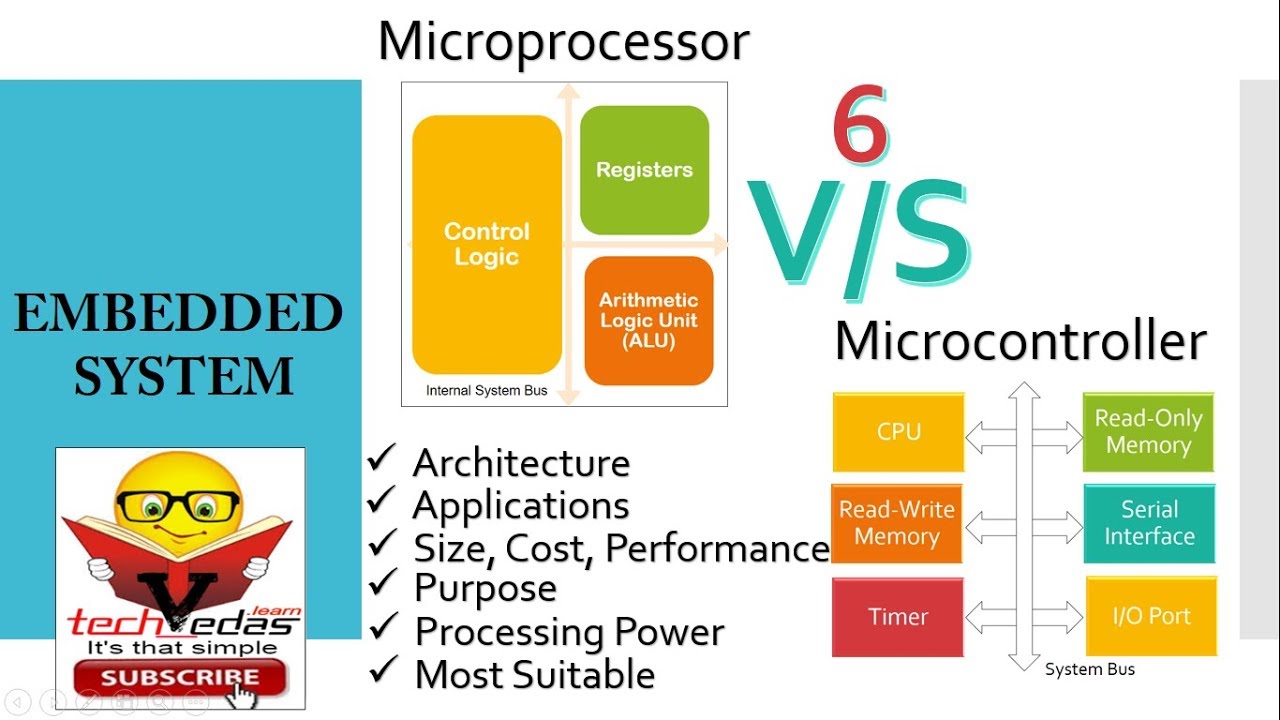
The processor core, RAM, ROM, and important peripheral components are housed in a single chip. The tasks include dedicated functions like controlling engine temperature in vehicles, displaying information in washing machines, etc. High clock speeds and bandwidths lead to faster processor operation and smoother communication with peripherals.įig 2: Detail Of A Computer Circuit BoardĪ microcontroller is a low-cost microcomputer that executes specific tasks in embedded systems. Three fundamental characteristics that differentiate microprocessors: the instruction set, clock speed, and bandwidth. It’s a versatile, programmable, register-based chip that accepts binary instructions from memory and processes input data to output. Thus, it performs all a central processing unit (CPU). Microprocessor: Costįig 1: Electronic Circuit Board With ProcessorĪ microprocessor is a computer processor housed in one integrated circuit (IC) or a single chip.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
